Smart Construction
ISSN: 2960-2025 (Print)
ISSN: 2960-2033 (Online)
CODEN: SCABAK
Contact
For any inquiries regarding journal development, the peer review process, copyright matters, or other general questions, please contact the editorial office.
Editorial Office
E-Mail: smartcon@elspub.com
For production or technical issues, please contact the production team.
Production Team
E-Mail: production@elspub.com
About This Journal
Numerical investigation of seismic performance and size effect in CFRP-reinforced concrete shear walls
Received
31 Dec 2024
Accepted
27 Mar 2025
Published
18 Apr 2025
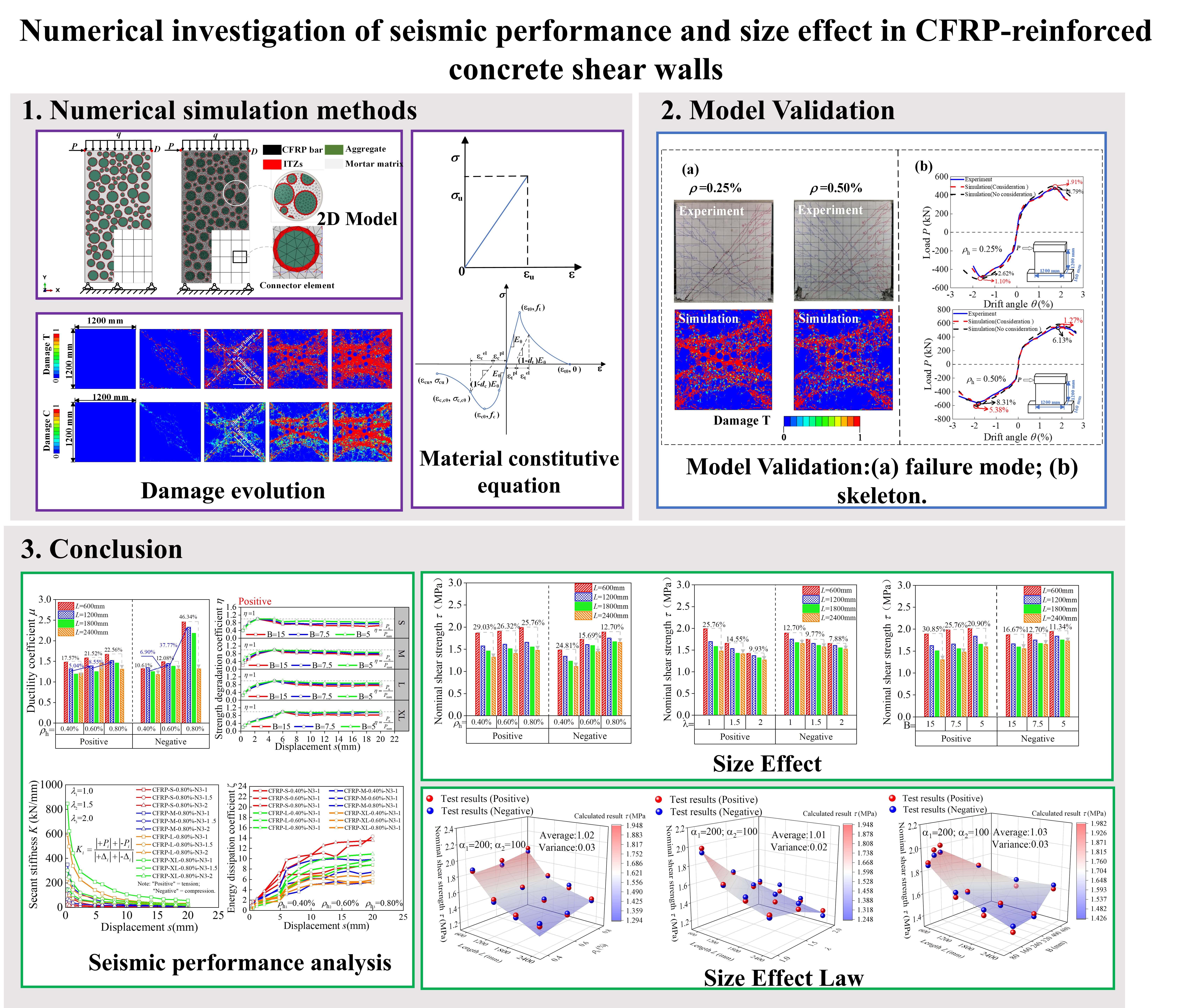
Addressing conventional reinforced concrete (RC) shear walls’ susceptibility to brittle failure and residual deformation during earthquakes; this study investigates carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP)-RC composites for enhanced seismic resilience. CFRP’s superior strength-to-weight ratio; corrosion resistance; and self-centering potential address post-earthquake reparability challenges. Current knowledge gaps persist in size-effect mechanisms under combined geometric and reinforcement parameters (shear span ratio; horizontal reinforcement ratio; height-to-thickness ratio). Numerical analysis of 28 models evaluates hysteretic behavior; strength degradation patterns; ductility coefficients; and residual deformation characteristics. A refined size-effect model incorporating CFRP’s strain distribution overcomes existing predictive limitations; advancing performance-based design of damage-tolerant structures.
Predicting bond-slip behaviour in grouted bellows connect rebar using deep learning
Received
06 Jan 2025
Accepted
18 Mar 2025
Published
18 Apr 2025
Grouted Bellows Connect Rebar (GBR) technology is critical for ensuring reliable connections in precast concrete components. The bond-slip behaviour, a core metric for assessing GBR connection performance, presents significant complexity, and existing empirical models often fall short in prediction accuracy to meet engineering demands. Addressing this challenge, this study introduces an innovative hybrid model (CNN-LSTM) that integrates convolutional neural networks with long short-term memory networks. Utilizing eight critical parameters, such as grouting strength, reinforcement ultimate strength, and the anchorage length-to-diameter ratio of the reinforcement, the model achieves precise predictions of GBR bond stress. This study systematically collected data from 114 sets of GBR pull-out tests, constructing a dataset comprising 2,272 bond-slip samples for model training and validation. Additionally, 15 GBR independent samples were independently fabricated and multiple samples were extracted to assess the model generalization capability. Experimental results demonstrate that the CNN-LSTM model significantly outperforms traditional empirical models in predicting bond stress and exhibits superior generalization across key metrics, including total energy consumption, maximum bond stress, failure modulus, and residual energy. Parameter importance analysis reveals that grouting strength, reinforcement ultimate strength, and the anchorage length-to-diameter ratio are the most influential factors in bond stress prediction. Building on the CNN-LSTM model predictions, this study establishes an improved empirical model with clear physical significance, offering a reliable computational foundation for engineering applications.
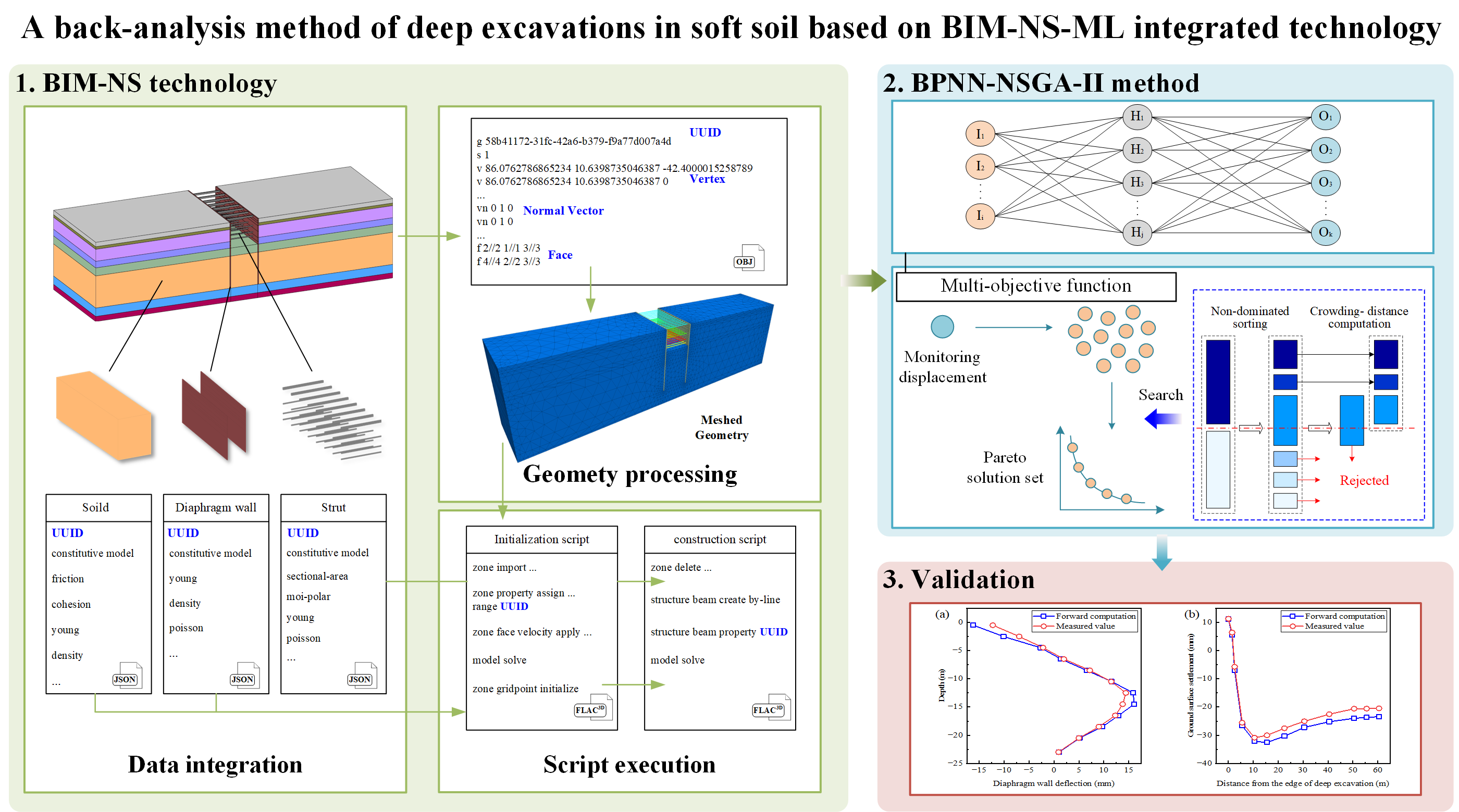
A back-analysis method of deep excavation in soft soil based on BIM-NS-ML integrated technology
Received
23 Dec 2024
Accepted
18 Mar 2025
Published
02 Apr 2025
It is witnessed that building information modeling (BIM) technology has shown its capabilities in data integration in the construction industry. Incorporating innovative geotechnical theories into BIM helps to further develop its application potential. In the practice of deep excavation engineering, obtaining accurate soil parameters is the key to preventing deep excavation accidents and reducing construction costs. Aiming at the complexity of soil properties in soft soil deep excavations, an intelligent inversion framework for soil parameters in deep excavations is established by using BIM technology, finite difference method (FDM), and nondominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II). Firstly, a building information modeling-numerical simulation (BIM-NS) integrated component is implemented based on a transformation interface, including geometric meshing processing and controlled script automated execution. Then, a back-analysis component based on NSGA-II optimization is attached to the BIM-NS processing to improve the accuracy of soil parameters. Subsequently, a framework of the building information modeling- numerical simulation-machine learning (BIM-NS-ML) integrated technology is established, enabling the usage of optimal soil parameters for automatic deep excavation simulation. Finally, the integrated framework is applied to a subway deep excavation project, which verifies that the proposed intelligent integration framework can accurately identify soil parameters in an efficient manner. The BIM-NS-ML integrated technology significantly improves the efficiency of modeling and calculating. The multi-objective optimization algorithm effectively addresses the problem of parameter complexity in soft soil. In addition, the intuitiveness of parameter inversion results is further enhanced to provide support for construction management and decision-making.
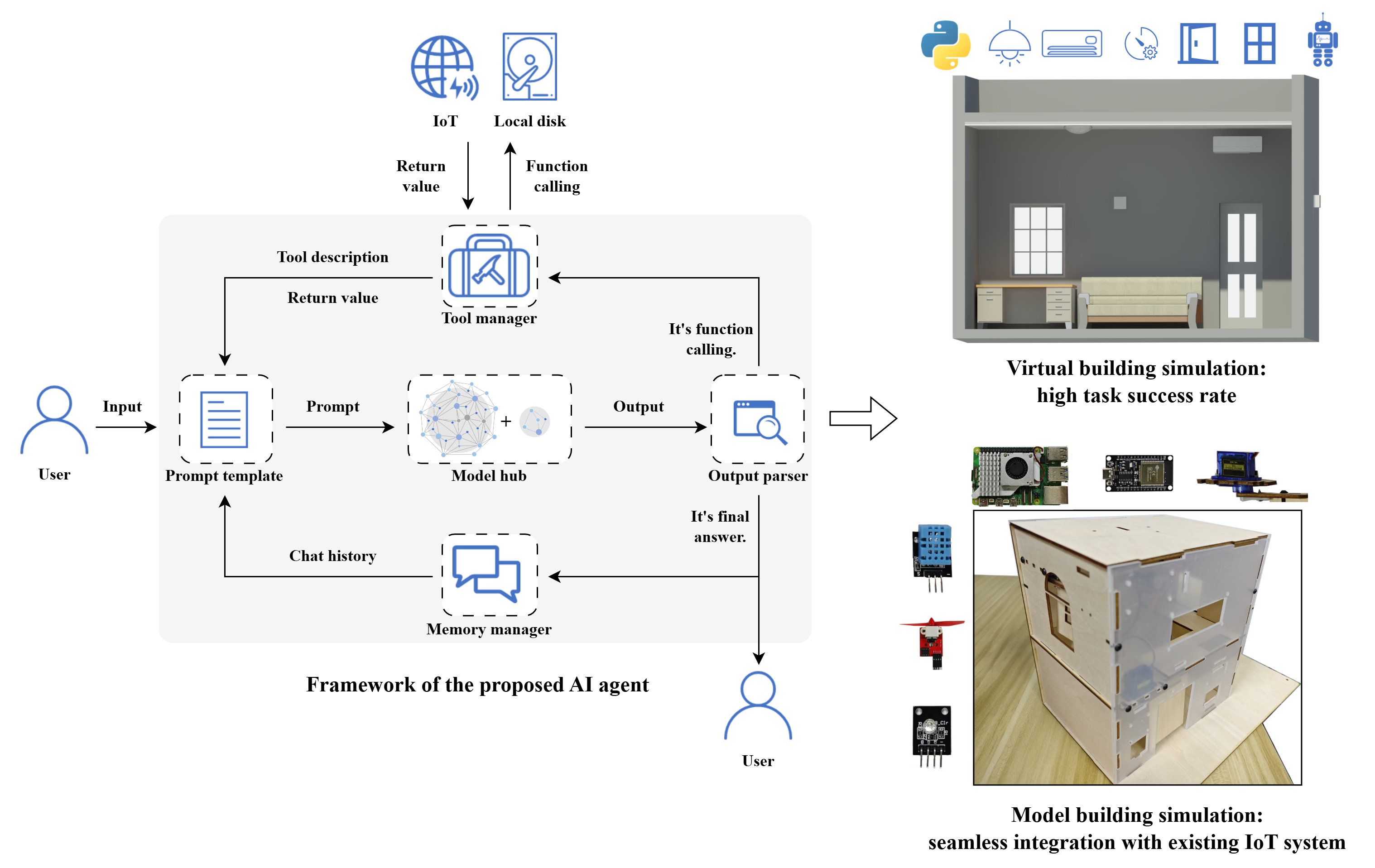
A general AI agent framework for smart buildings based on large language models and ReAct strategy
Received
25 Dec 2024
Accepted
19 Feb 2025
Published
04 Mar 2025
Smart buildings represent a significant trend in the future of the construction industry. The performance of human-computer interaction plays a vital role in achieving this from a human perspective. However, existing human-computer interaction algorithms are often limited to simple commands and fail to meet the complex and diverse needs of users. To address this issue, this paper introduces large language models (LLMs) and AI agents into smart buildings, proposing a general AI agent framework based on the ReAct strategy. The LLM serves as the system’s brain, responsible for reasoning and action planning, while tool calling mechanism puts the LLM’s plans into practice. Through this framework, developers can rely on prompt engineering alone to enable the LLM to interpret user intent accurately, perform appropriate actions, and manage conversation history effectively, without any pre-training or fine-tuning. To examine this framework, an experiment was conducted in a virtual building, which showed that the proposed agent successfully completed 91% of simulated tasks. Additionally, the agent was deployed on a single-board computer to control devices in a model building, demonstrating its effectiveness in the real world. The successful operation of the agent in this environment highlighted the potential applications of the proposed framework using existing IoT systems, providing a new perspective for the upgrading of human-computer interaction systems in smart buildings in the near future.
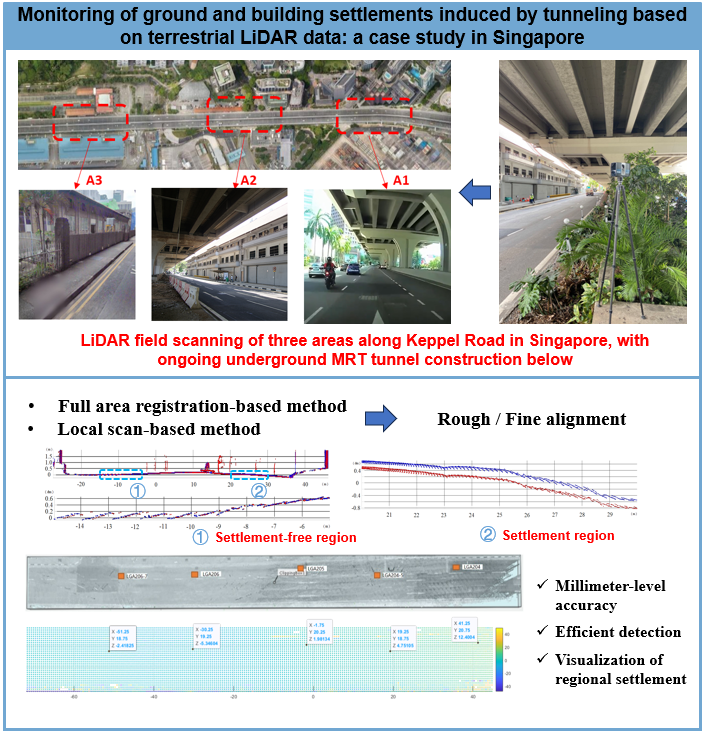
Monitoring of ground and building settlements induced by tunneling based on terrestrial LiDAR data: a case study in Singapore
Received
03 Dec 2024
Accepted
07 Feb 2025
Published
20 Feb 2025
Ground and building settlements induced by tunneling excavation are common in cities. Such settlements can cause instability of the ground and threaten the safety of the upper infrastructures or buildings. Hence, it is vital to monitor the settlements during tunnel excavation to identify any potential risk. The current approach for settlement monitoring relies on manual measurements, which suffers from low efficiency and high labor cost. To improve monitoring efficiency, this study presents a settlement monitoring method based on terrestrial LiDAR data, which mainly consists of rough and fine alignment steps. Algorithms are developed to automatically process the 3D point cloud data obtained from terrestrial LiDAR and obtain settlement values for grounds and buildings. The proposed technique was applied and validated in a region with on-going tunneling works in Singapore. Different monitoring strategies including local-scan based method and registration-based method were examined and compared in this case study. Results demonstrated that the local scan-based monitoring method could yield more accurate settlement measurements compared with the traditional survey method. Registration-based method had higher calculation efficiency but with insufficient accuracy. In general, it is demonstrated that the LiDAR based settlement monitoring method is feasible in engineering practice, with measurement errors controlled within 2–3 mm, and has great potential to improve efficiency and reduce labor cost required by the traditional method.
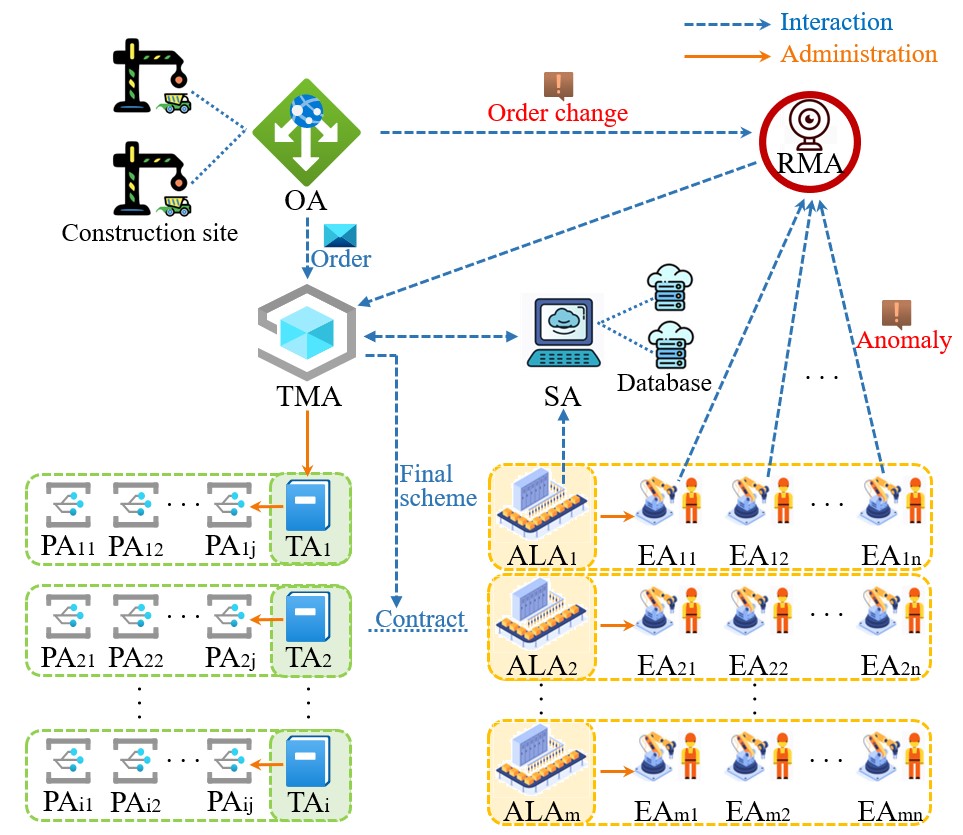
Swarm-intelligence collaboration based regular scheduling and dynamic rescheduling of precast component production: in prefabricated building project management
Received
04 Nov 2024
Accepted
28 Jan 2025
Published
17 Feb 2025
The production of precast concrete (PC) component in factory is a very influential and complex work for the construction of the project. The rhythm of production is often delayed because the production process in most PC component factories is discrete at present. This study focuses on the production process of PC components and aims to propose regular scheduling and dynamic rescheduling models in prefabricated building project management. Based on the swarm-intelligence (SI) collaboration mechanism, the dynamic-interval synergy auction (DISA) strategy is proposed to improve contract net protocol (CNP). The genetic algorithm based on Tchebycheff (TCH) decomposition strategy is used to obtain the optimal production scheduling schemes. In addition, this model designs a coding mechanism for components based on Omniclass classification standard and the attributes of components are extended based on IFC extension mechanism. This model was verified in a PC factory. The experimental results showed that the decentralized negotiation mode with dynamic time window mechanism can avoid local optimization of schemes. Compared with traditional calculation method, this method could obtain more comprehensive and lower cost schemes. Based on the collaboration mechanism, with improved CNP and TCH strategies introduced, the dynamic model can improve the integrity and intelligence of PC factory.
GIS based solutions for management of public building and infrastructure assets: a review of state of the art and research trend analysis
Received
14 Feb 2025
Accepted
07 Apr 2025

.png)